Abstract
If we google Exchange-Traded Funds, the dictionary at the top of the page shows that ETFs are the type of investment funds traded on a stock exchange.
Exchange-traded funds are commercial securities that track particular indexes; they could be commodities, bonds, or a basket of assets (e.g., index funds). In other words, ETFs are funds that track indexes such as CNX Nifty or BSE Sensex, etc.
Introduction
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) offer advantages over stocks in two different stages. At once, the return from stocks in the sector or industry has a narrow dispersion around the mean. The Second is when investors cannot gain an advantage through knowledge of the company, and an ETF could be the best choice for investors in both situations.
ETFs
As the name suggests, Exchange-traded Funds are funds that trade on exchanges and generally track a specific index. When someone invests in an ETF, they get a bundle of assets they can buy or sell during market hours—potentially lowering the risk while helping to diversify their portfolio.
ETFs can track anything from the price of commodities to a diverse collection of securities, which suit institutional and individual investors. An ETF can even be structured to track specific investment strategies.
We see daily fluctuations in ETFs prices as market participants buy or sell the ETFs, and this differs from mutual funds (financial investment mechanism that pools assets from shareholders to invest in securities like stocks, bonds, money market instruments, and other assets Which only trade once a day after the market closes and we can’t trade them on exchanges).

ETFs include investments in all possible forms, including commodities or bonds, and have low expense ratios and fewer broker commissions than when someone buys or sells the stocks individually.
An ETF fund is a like a basket of multiple assets with different prices rather than only one, like what we see in stock trading. There are various assets within an ETF, so they can be a popular choice for those who want to follow a risk management strategy.
An ETF could include a broad range of assets from different industry sectors or be limited to particular industry assets, some are exclusively for the US market, and others will be available for international trading.
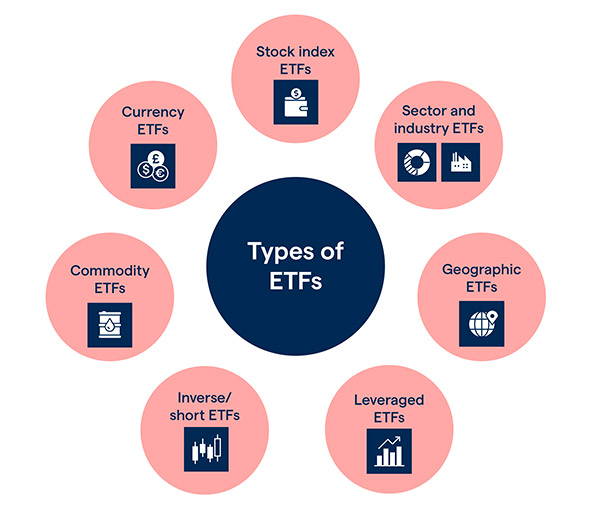
Different Types of ETFs
- Passive ETFs
Passive ETFs replicate a broader index’s performance and follow a specific targeted sector or trend. - Active ETFs
Oppositely actively managed ETFs do not target an index of securities. Instead, portfolio managers decide which securities to contain in the portfolio. However, active ETFs are more expensive to investors but have benefits over passive ETFs. - Bond ETFs
It is better for investors looking for a regular income to choose Bond ETFs. Bond ETFs give investors distribution income depending on underlying bonds’ performance. Bond ETF investors may prefer municipal bonds. Bond ETFs trade at a “premium or discount” from the actual bond price, and contrary to their underlying instruments, bond ETFs do not have a maturity date. - Stock ETFs
Stock (equity) ETFs include a basket of stocks in a single industry or sector. Stock ETFs have lower fees than mutual funds, and investors do not involve in actual ownership of securities. The characteristics of Stock ETFs make it suitable for investors seeking a regular income to choose Bond ETFs, and their income distribution depends on the performance of underlying bonds. - Industry (Sector) ETFs
We call funds that focus on specific industries sector ETFs or industry ETFs (e.g., Energy sector ETFs that include companies involved in the energy sector). - Commodity ETFs
As comes from their name, commodity ETFs invest in commodities such as gold and crude oil. Commodity ETFs benefit investors by diversifying a portfolio and making it easier to hedge downturns.
Commodity ETFs provide a cushion during a slump in the stock market, and holding shares in a commodity ETF is cheaper than physical possession of the commodity. This is because the former does not involve insurance and storage costs. - Currency ETFs
Currency ETFs refer to pooled investment vehicles that follow the performance of currency pairs consisting of fiat money and foreign currencies. Investors can use currency ETFs to speculate on currencies’ prices based on a country’s political and economic developments. Currency ETFs also diversify a portfolio, hedge against volatility in forex markets, or even hedge against the threat of inflation. In the past few years, cryptocurrencies, especially Bitcoin, have also been considered in this type of ETF. - Inverse ETFs
Investors in inverse ETFs attempt to earn from stock declines by shorting stocks. Shorting is selling a stock, expecting a decline in value, and purchasing it at a lower price again. Inverse ETFs use derivatives to short a stock and are bets that the market will decline. Once the market declines, an inverse ETF increases by a proportionate amount. Investors must consider that many inverse ETFs are ETNs (so-called Exchange-Traded Notes are unsecured debt securities that track an underlying index of securities and trade on major exchanges like a stock.) - Leveraged ETFs
Leveraged ETFs follow a mechanism that uses multiples on the return of the underlying investments. A Leveraged ETF uses derivatives such as options or futures contracts to leverage their returns, and leveraged inverse ETFs, which seek an inverse multiplied return. - Bitcoin ETFs
However, Bitcoin is in its early years as a financial instrument. Still, it was challenging traditional financial markets with several thousands of dollars of value and fluctuant price nature, representing a new era in financial markets based on blockchain industry derivatives.
When ETF funds and Bitcoin cross a common point in the market, trading and exchanging securitized Bitcoin or assets that directly relate to Bitcoin or Bitcoin price on traditional exchanges instead of cryptocurrency exchanges, it will form a Bitcoin ETF.

Below, we provide this article’s audiences with a list of the top 5Bitcoin ETFs, which are mainly US based. (forbes.com)
- Bitwise Crypto Industry Innovators ETF (BITQ)
- Global X Blockchain ETF (BKCH)
- Siren Nasdaq NexGen Economy ETF (BLCN)
- Amplify Transformational Data Sharing ETF (BLOK)
- First Trust SkyBridge Crypto Industry and Digital Economy ETF (CRPT)
Conclusion
An ETF is a basket of securities that investors purchase or sell on a stock exchange. ETFs, help investors make money by investing in stocks or bonds when assets within the fund, such as stocks, grow in value or pass on profits to investors through dividends or interest.
ETFs are funds that track indexes such as CNX Nifty or BSE Sensex, etc.
ETFs are efficient ways to diversify portfolios without having to select individual stocks or bonds, give investors and cover most major asset classes and sectors, including; Passive and Active ETFs, Bond ETFs, Stock ETFs, Industry (Sector) ETFs, Commodity ETFs, Currency ETFs, Inverse ETFs, and Leveraged ETFs.
