Abstract
Alpha investment strategy refers to the ability of an investor to beat the market or its “edge”. “Excess Return” and “Abnormal Rate of Return” are other names for this investment strategy. The idea behind the Alpha investment strategy is that markets are efficient.
Beta Investment Strategy (so-called Smart Beta) measures a stock’s sensitivity to the movement of the overall stock market. Beta is an investment strategy in which an enhanced indexing strategy seeks to exploit certain market index performance factors, which makes smart Beta fundamentally different from other traditional investment strategies.
As mentioned earlier, the alpha investment strategy has another Conjunction: the Beta investment strategy. In this article, we are trying to discover these two investment strategies and their advantages and disadvantages.
Introduction
Investment is an investor’s act when they acquire or invest in a financial instrument like securities, currencies, commodities, precious metals, etc., to obtain more revenue or profit from the investment over a specific time. Investment strategies help investors to increase their wealth or save money from the potential risks in the market.
History of Investment
The first investing principles are rooted in the Code of Hammurabi, written around 1700 BCE in modern Iraq, that in those times was named Mesopotamia. This historical code provided the framework that includes many civilization rules, including the legal framework for investment. It explains how merchants and investors must pledge collateral to invest in projects.
For example, they could pledge a piece of land as collateral, and anyone who broke obligations was sentencing to the punishment. Other historical documents show that there were laws for investing in Europe in the 17th century.

Carving of the code of king hammurabi from Iraqi money
What is Investment?
Investment is an investor’s act when they acquire or invest in a financial instrument like securities, currencies, commodities, precious metals, etc., to obtain more revenue or profit from the investment over a specific time. Investment strategies help investors to increase their wealth or save money from the potential risks in the market.
What are Investment Strategies?
Investment strategies help investors to choose when, where, and how to invest to receive the expected return, minimize the risk of investment and plan for corpus amount, long-term, short-term holdings, retirement age, choice of industry, etc.
Most important investment strategies
- Passive and Active Strategies.
- Growth Investing (Short-Term and Long-Term Investments).
- Value Investing.
- Income Investing.
- Dividend Growth Investing.
- Contrarian Investing.
- Indexing.
Note: For more information, please visit wallstreetmojo.
What is the α Investing Strategy?
Alpha refers to excess returns earned against investment above the benchmark’s return. In this approach, investors seek to generate Alpha in diversified portfolios, with diversification intended to eliminate unsystematic risks. Alpha strategy is a mechanism in which the performance of a portfolio relative to a benchmark and often considered to represent the value that a portfolio manager adds to or subtracts from a fund’s return.
Mechanism of Alpha strategy
Alpha is a symbol of the market performance in the market, in which market participants or strategists decide to beat the market. The mechanism estimates the investment return by studying the behavior of a benchmark or an index in the market. Through Alpha strategy, strategists or traders generalize it to the market movements as a whole.
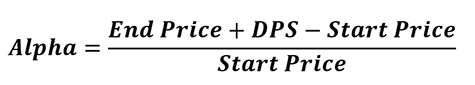
What is Jensen’s measure or Jensen’s Alpha?
Jensen’s Alpha is a statistical risk-adjusted performance measure that attempts to quantify the Alpha in a portfolio and represents the average return on a portfolio or investment, above or below that predicted by the capital asset pricing model (CAPM). This measure assists investors or strategists in measuring the portfolio or investment and the average market return. The short form of Jensen’s Measure or Jensen’s Alpha is Alpha.
Who must choose Alpha?
End price, DPS (which stands for Distribution/Share), Start price.
Suppose someone plans to invest in mutual funds and wants to select the fund that has consistently surpassed the overall stock market. Alpha is a good choice that simply measures volatility. Alpha is a criterion for a portfolio manager to estimate market indices and determine how well they perform.
What is the β (Smart Beta) Investing Strategy?
Smart Beta is where the benefits of passive investing and the privileges of active investing are combined to benefit traders, investors, and strategists.
In other words, the Beta strategy is the more ingenious version of the Alpha strategy, with a better performance. It is because, in the Beta investment strategy, traders, investors, or strategists consider less risk when they increase the diversification at a more reasonable cost compared to the old investing management methods, which benefit more from straight index investing.
The mechanism of the Smart Beta
The Smart Beta is a method for people seeking to combine the benefits of passive and active investing strategies by using index construction rules instead of traditional market capitalization-based indices. The Smart Beta approach investigates volatility, liquidity, quality, value, size, and momentum, which is why it is becoming more popular daily.
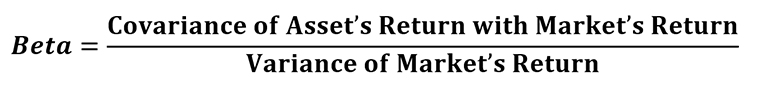
Who must choose Beta?
CR (which stands for Covariance of asset’s return with market’s return), Variance of market’s return.
Beta is an indicator that measures the relative volatility of an investment. Suppose an investor, strategist, or trader doesn’t like volatile assets. In that case, they can use the beta, which is an approach that assists them in identifying the right instrument for investments because it is an indication of its relative risk.

Alpha vs. Beta
When investment exceeds its benchmark, we call that Alpha which seeks to generate returns and is irrelevant to the stock market. The Beta is the benchmark that matches the overall market’s performance.
Conclusion
Alpha and Beta are both historical measures of past performances. Alpha indicates how good or bad the stock has performed compared to benchmark indices, and always a high alpha is good from an investor’s POV. An investor may prefer a high Beta in growth stocks, but they also may ignore it if they prefer less risk and look for steady returns.
