The act of using considerable computing power in a blockchain network to verify and validate a block of cryptocurrencies through solving several complicated mathematical puzzles nevertheless mine a block with reward, or mining an orphan block is mining. As the speed of validating the new block to add to previously validated blocks is a determinative factor, miners gather in an entity known Mining Pool to accelerate their hashing power and increase the speed of validating the new block. However, they have to share the block’s reward among them besides paying Mining Pool services fees, but this way, they are guaranteeing their reasonable reward, which is a more feasible strategy most of the time.
Introduction
When someone adds a block to a chain of blocks through solving cryptographical puzzles, which essentially are mathematical equations, we call them a miner, and their act is crypto mining, but when two or more miners join to increase their hash power and accordingly, their chance to mine an available block to earn the reward, the place where there are joining is called Mining Pool.
What is (Cryptocurrency) Mining?
Mining is a Peer-to-peer computational procedure in which several linked computers or other types of computing processors units work to verify and validate cryptographical transactions. There are specific blockchain networks (i.e., Bitcoin Network, Ethereum) where all done transactions will be recorded in all participating nodes across that particular blockchain.
There are some approaches for mining cryptocurrencies, and there are many networks with different digital currencies. However, some coins or tokens could be mined and traded through other networks through the same protocols like ERC-20, BEP-20, etc. One of the essential factors in mining cryptocurrencies is a mining difficulty which depends on the market price of that specific cryptocurrency and people interested in mining or trading that particular coin. How much the number of interested people in one particular cryptocurrency increases, the difficulty of that specific network also increases.

There are different methods based on hardware and software for people who have decided to mine cryptocurrencies;
GPU and CPU miners consume more energy than ASIC miners. They are also flexible to mine different cryptocurrencies when ASIC miners cannot accomplish that task through the defined algorithm. GPU miners, which are Graphic cards, are more affordable for everyone than ASIC miners, and the leading hardware manufacturer can manufacture lots of them regularly and send them to the market.
ASIC miners are much more efficient than GPU miners. As long as ASIC mining increases the speed of the mining process, miners are more eager to use ASIC miners, and the number of ASIC miners increases as well. The difficulty and the Hash rate increase how much the mined cryptocurrencies through a network increase.
FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Arrays) is a circuit of hardware programmable by users with specific software to do a logical process to achieve a result. The software/program and the user could delete and change the program to define a new task for the system. Using FPGA is reasonable because of the higher speed of mining and less energy than GPU and CPU mining approaches. However, they are not available as much as GPU or CPU equipment.
Cloud mining is when someone wants to mine a block using cloud facilities. In this method, service users dont need to purchase and install any hardware and relevant software. Many companies let people register and use mining hardware remotely against an agreed fee for an agreed period to buy HASH power; in this method, the cloud mining services member doesn’t need to pay maintenance costs or does not pay any direct electricity bill.
The most critical element in crypto mining is the chance of validating the new block, which needs to overcome the network difficulty and solve the abovementioned cryptographical mathematical puzzles.
What are a Mining Pool and the Advantages of Joining a Mining Pool?
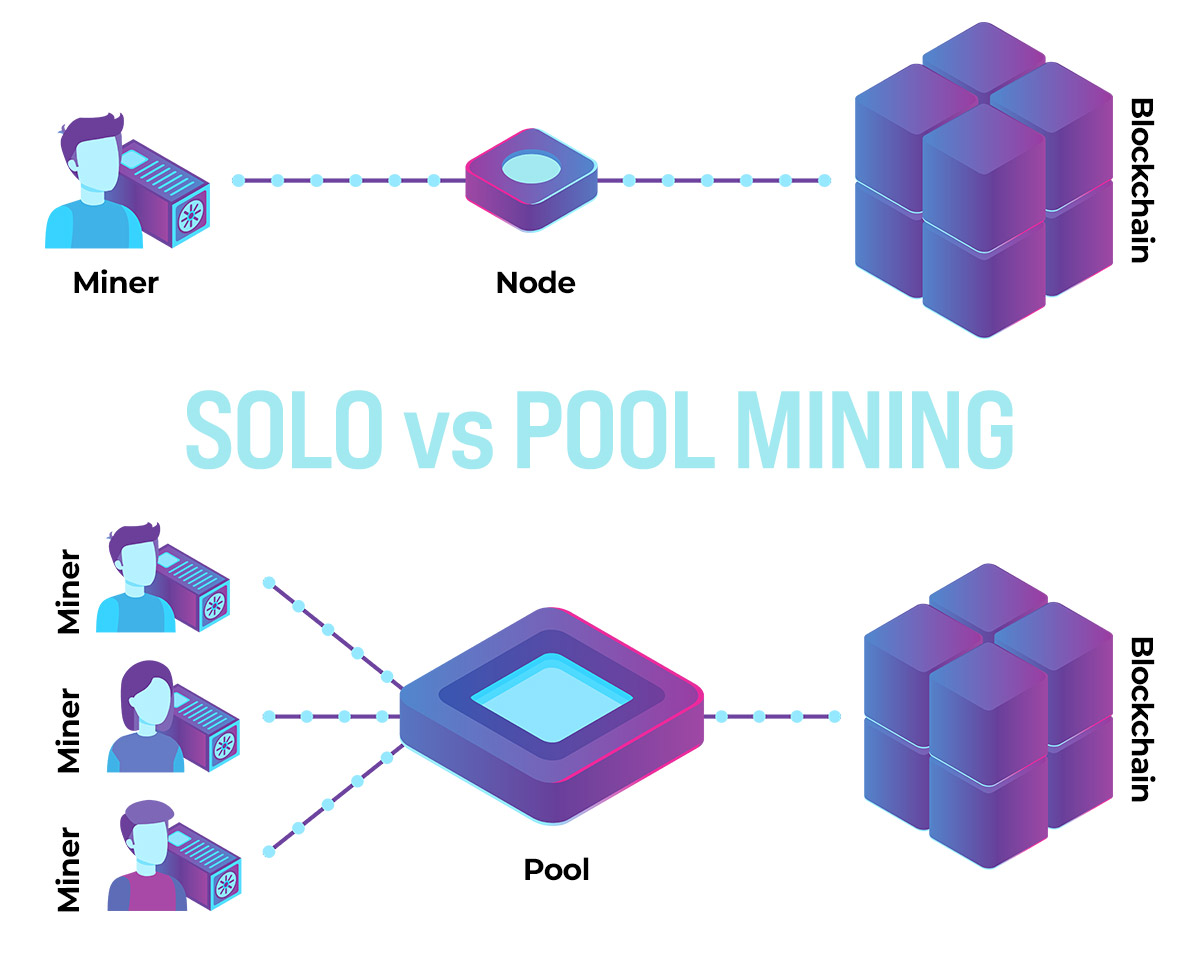
When miners join a system that helps them accelerate their computational power to increase their chance to mine a block of a blockchain network, they have entered a system that we will call the mining pool hereunder.
What is a Mining Pool?
A mining pool is a point in common that cryptocurrency miners ( a big mining rig or one or two mining units) join to boost their hashing speed and increase their chance to mine a block by increasing their computational power, which increases their chance to mine a block.
Why Joining a Mining Pool is Good?
Depending on the method they have chosen, Miners will receive almost a sustainable revenue. There are more than ten payment methods, but we will investigate the most common methods among them.
- CPPSRB: Capped Pay Per Share with Recent Backpay.
- DGM: Double Geometric* Method.
- ESMPPS: Equalized Shared Maximum Pay Per Share.
- POT: Pay on Target.
- PPLNS: Pay per Last N Shares.
- PPLNSG: Pay per Last N Groups.
- PPS: Pay per Share.
- Prop: Proportional.
- RSMPPS: Recent Shared Maximum Pay per Share.
- SMPPS: Shared Maximum Pay Per Share.
- FPPS: Full Pay per Share.
*Geometric reward types that enable an operator to absorb some of the variance risks.
When every single miner combines hash power with other miners in a mining pool, it increases their chances of successfully mining a block. In addition, a mining pool helps to lower the buoyancy of payouts, rather than waiting for large payouts when a miner successfully mines their block to add to the chain of blocks.
They can collect a small part of the pool’s rewards more frequently. On the other hand, miners in a mining pool can generate blocks more quickly due to increased computational power, which produces a consistent and steady reward stream rather than irregular or one-off rewards. Joining a mining pool reduces the costs of mining procedures because mining alone requires allocating a large area to install mining units. The processors’ power consumption generates heat and requires an effective ventilation system.
The cost of the allocated space and the energy bill makes this process costly however it’s very likely that mine a block of bitcoin covers the expenses, but all miners singularly aren’t that lucky to mine a block of Bitcoin whenever they want, and here joining a mining pool increases the chance of mine a block through an alliance among miners who join a mining pool. Joining a mining pool reduces mining costs due to the reducing waste of money spent and increases the chance of mining a block. They share the reward and pay mining pool service fees, but it is still worthwhile.
What is a Smart Mining Pool?
A “smart mining pool” is a mining pool that lets the client mine different cryptocurrencies with the same algorithm. It automatically switches to the cryptocurrency on the network with a higher value from time to time to maximize its clients’ profits.
What is Cloud Mining?
When miners join a cloud mining system (mainly through a website or application), they have a chance to mine the profitable cryptocurrency they have chosen (which must be among the offered digital currencies on the website) and receive their share of the mined block of the cryptocurrency, against the service fee they have paid to the services provider. In cloud mining, participants do not have any concerns about equipment maintenance or electricity bill costs.
Models of Cloud Mining
Host Mining
Host mining is the most regular cloud mining model, in which the client leases or purchases the hardware located in the cloud mining facilitator’s place, and it seems that the customer is responsible for mining equipment during the contract.
Leased Hash Power
In this model, the participant rents or leases a mining farm’s hash power or computing power. This method is more regular for mining coins except for Bitcoin “Altcoins,” Each participant gets the shares according to the hash power they have rented from the mining farm.
Solo Mining
Solo Mining is an act of verifying and validating a block solely to earn the profit of the mined block alone and only pays the service costs. As in cryptocurrency mining, many participants are working on the blockchain network and competing with other miners to add the newly mined block to the chain of previously mined blocks. Increasing the hash power by joining a mining pool could be a considerable help for miners who invest their time and find.
Conclusion
When people who are mining through cloud mining or those who are mining locally in their mining rigs across the globe decide to combine their computing power (hash power), they join a point which we call “Mining Pool,” to solve mathematical puzzles to mine a block and add to the previously mined block of the blockchain. There are different payout methods that users can choose what most meets their needs.
